第二届信息通信及安全数学理论年会
暨信息通信及安全数学理论委员会第一届第三次全体会议
中国.西安
2024年4月19日—4月21日
主办单位:中国通信学会信息通信及安全数学理论委员会
承办单位:西安电子科技大学
会议日程
会议地点:西安电子科技大学南校区网安大楼会议中心101。
腾讯会议号:656 7183 2797(密码:123456)
4月20日上午 |
8:30—8:35 主持人:王子龙 |
开幕式 |
上午第一节 主持人:宗传明 |
时间 |
报告人 |
题目 |
8:35—9:15 |
喻杨 |
Cryptanalysis of the Peregrine Lattice-Based Signature Scheme |
9:15—9:55 |
王安宇 |
Exploiting the Symmetry of 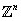 : Randomization and the Automorphism Problem : Randomization and the Automorphism Problem |
9:55—10:20 |
合照、茶歇 |
上午第二节 主持人:王美琴 |
时间 |
报告人 |
题目 |
10:20—11:00 |
路献辉 |
密码发展新方向及其数学原理 |
11:00—11:40 |
胡凯 |
从结构到代数:积分分析的历史与最新进展 |
11:40 |
午餐(地点:西电南校区丁香餐厅三楼) |
4月20日下午 |
下午第一节 主持人:胡红钢 |
时间 |
报告人 |
题目 |
14:00—14:40 |
李震国 |
LEGO-Prover: 基于大语言模型的自动定理证明 |
14:40—15:10 |
讨论与提问 |
15:10—15:30 |
茶歇 |
下午第二节 主持人:周正春 |
时间 |
报告人 |
题目 |
15:30—16:10 |
王涵 |
Large Atomic Model |
16:10—16:40 |
讨论与提问 |
16:40—17:40 |
信息通信及安全数学理论委员会第一届第三次全体会议 |
18:00 |
晚餐(地点:西电南校区丁香餐厅三楼) |
4月21日上午 |
上午第一节 主持人:侯庆虎 |
时间 |
报告人 |
题目 |
9:00—9:40 |
光炫 |
安全网络函数计算 |
9:40—10:20 |
上官冲 |
When can a binary expander code correct 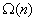 errors in errors in 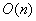 time time |
10:20—10:40 |
茶歇 |
上午第二节 主持人:冯涛 |
时间 |
报告人 |
题目 |
10:40—11:20 |
马立明 |
Optimal and asymptotically good locally repairable codes via algebraic curves |
11:20—12:00 |
温金明(在线) |
Prompt as Triggers for Backdoor Attack: Examining the Vulnerability in Language Models |
12:00 |
午餐(地点:西电南校区丁香餐厅三楼) |
报告摘要
安全网络函数计算
光炫
南开大学
该报告将介绍安全网络函数计算问题以及近来的研究进展。安全网络函数计算研究如何在通信网络上安全地计算目标函数,其核心问题是安全网络函数计算容量的刻画,包括容量界和码构造。然而,对于安全网络函数计算的一般性模型,该容量的刻画是极其困难。本报告的研究工作聚焦于线性目标函数,给出了该容量的普适上界(适用于任何网络拓扑和安全级别)、上界的高效计算方法以及码构造方案;并完全刻画了多类模型的容量。
个人简介:光炫,南开大学数学科学学院教授,博士生导师,南开大学数学学科学术委员会委员、教育部“核心数学与组合数学”重点实验室固定研究人员;入选国家青年人才项目、香江学者计划、天津市131创新人才计划第二梯队、天津市“三年千人”高层次人才引进计划和南开大学百名青年学科带头人培养计划(A类)。2012年毕业于南开大学陈省身数学研究所,获博士学位,曾在美国南加州大学信息科学研究所及香港中文大学网络编码研究所从事研究工作近5年。光炫博士的研究兴趣为信息论、编码理论与密码学;目前的研究方向为面向函数计算的信息论和编码。近年来出版一部学术专著(一作),由德国Springer出版;发表学术论文60余篇,其中在信息论顶刊IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory上发表论9篇(其中8篇为双栏18页(单栏约40页)以上长文),在信息论、安全和通信理论的权威期刊和会议上发表论文20余篇,包括IEEE J. Sel. Areas Inf. Theory, IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun., IEEE Trans. Inf. Foren. Sec., IEEE Trans. Commun., USENIX Security,《中国科学》等。获多个国内外会议的最佳论文奖;获天津数学与统计“青年学者奖”,中国电子学会“信息论青年新星奖”等。主持重点研发计划课题和基础加强重点研究课题等省部级基金项目8项,获田家炳教育基金资助;主持华为公司和中海油服物探研究院科技项目2项。
从结构到代数:积分分析的历史与最新进展
胡凯
山东大学
由于结构简单、加密效率高,对称密码算法是数据加密的最主要工具。密码分析是保证对称密码算法的唯一手段。在众多的分析方法中,积分分析是最主要的分析方法之一。积分分析最初被认为是算法的一种结构性质,后来,其与对称密码算法代数性质的紧密关系被逐渐发现。一系列探测积分性质的工具被发明出来,其中最重要的是分离特性和其自动化分析方法。尽管分离特性已经间接反映密码算法的代数结构性质,但是其与密码算法的代数正规型之间的关系一直较为模糊。单项式预测技术直接从密码算法的代数正规型出发,通过简单直接的路径传播关系,对分离特性进行了代数化解释,完全明确了分离特性与代数正规型之间的关系。单项式预测技术已经被应用于探测分组密码算法的积分性质和流密码和认证加密算法的立方攻击中。本次报告将介绍积分分析的发展历史和其最新进展,包括核心单项式预测技术和单项式预测技术在有限域上的扩展。
个人简介:胡凯,山东大学网络空间安全学院研究员,齐鲁青年学者。本科毕业于山东大学数学学院,2021年取得网络空间安全博士学位,师从长江学者王美琴教授。曾在新加坡南洋理工大学完成2年博士后研究,合作导师为多项ISO标准算法设计者的Thomas Peyrin教授。研究方向为对称密码算法的设计与分析,在密码学五大顶会欧密、亚密、FSE等发表论文20余篇。代表性工作有单项式预测技术、概率性高阶差分线性攻击等。博士论文获评2022年中国密码学会优秀博士论文,参与设计的分组密码算法Ballet获得中国密码学会算法竞赛一等奖。
LEGO-Prover: 基于大语言模型的自动定理证明
李震国
华为诺亚方舟AI基础理论实验室
大模型呈现出尺度定律,性能随着数据、模型、算力增大显著提升。很多领域因此正在发生范式转移,包括AIGC和科学发现。在这次报告中,我们将分享大语言模型在数学定理证明上的一个项目实践,LEGO-Prover。借助于形式化验证系统如Lean和Isabelle,LEGO-Prover可以从零开始或者从已被证明的定理库中学习如何证明定理、自动发现和生成可复用的引理,并在评测基准MiniF2F上取得了当前业界最好的成绩。可以预见,随着大模型技术的不断发展,形式化系统的不断完善,以及数学领域知识的不断数字化,数学有可能成为AI技术应用和发展的一个主要领域。
个人简介:李震国博士是华为诺亚方舟AI基础理论实验室主任,香港科技大学计算机科学和工程系的兼职教授。在加入华为之前,他曾在哥伦比亚大学电气工程系担任副研究员。他在北京大学获得数学学士和硕士学位,在香港中文大学获得机器学习博士学位。他的研究兴趣包括机器学习和人工智能。他入选AI 2000 Most Influential Scholars (by Aminer),Top 2% Most Highly Cited Scientists (by Stanford University),并担任NeurIPS 2023和ICLR 2024领域主席。
密码发展新方向及其数学原理
路献辉
中国科学院信息工程研究所
现代密码构建于数学和计算复杂性理论之上,基于单向函数及其同态性质构造了丰富的密码原语体系。当前,新一轮信息领域科技革命呈现多点突破交叉融合态势,量子计算、人工智能、6G通信等信息技术变革对密码学现有设计思想和方法提出新的挑战。为了解决这些挑战,现代密码理论体系需要在新的威胁模型下重构,在新的安全资源和功能维度下扩张,这些工作正在推动密码学进入新一轮变革性发展期。本报告将介绍抗量子密码、全同态密码、物理层密码、智能化密码等密码新方向及其背后的数学原理。
个人简介:路献辉,中科院信息工程研究所研究员,2009年于西南交通大学获得信息安全专业博士学位,2009-2012年进入中科院信息安全国家重点实验室从事博士后研究,2012年进入中科院信工所。主要研究兴趣包括可证明安全理论、抗量子密码、全同态密码、物理层密码,带领团队设计了抗量子密码算法LAC参加美国抗量子密码标准征集工作,是进入第二轮的26个候选算法之一。设计了门自举、电路自举、AES同态评估等核心算法的优化方案,研究成果发表于欧密2024和TCHES2024。融合物理层安全资源和现代密码学思想,提出了物理层密码设计理念。担任国际标准化组织ISO/IEC密码工作组专家,参与抗量子密码和全同态密码领域的国际标准化工作。
Optimal and asymptotically good locally repairable codes via algebraic curves
马立明
中国科学技术大学
Constructing optimal locally repairable codes is a challenging and interesting task and has attracted great attention in the last decade. Tamo and Barg gave a breakthrough result in this topic by cleverly considering good polynomials and subcodes of Reed-Solomon codes. Such a method can be generalized to construct locally repairable codes via automorphism groups of algebraic curves and subcodes of algebraic geometry codes. In this talk, I will introduce the constructions of optimal locally repairable codes via automorphism groups of elliptic curves over finite fields and asymptotically good locally repairable codes exceeding the Gilbert-Varshamov bound via the tower of Garcia-Stichtenoth curves. In particular, we can construct optimal locally repairable code with length up to 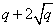 and large minimum distances which can be linear in its length.
and large minimum distances which can be linear in its length.
个人简介:马立明,中国科学技术大学数学学院副研究员,主要研究方向为编码理论和代数数论。理论上研究有限域上代数曲线的有理点和自同构群,应用于代数几何码,局部修复码以及序列中,得到了一批深刻的成果。在国内外知名期刊《Trans. Amer. Math. Soc.》、《IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory》、《IEEE Trans. Commun.》、《J. Combin. Theory Ser. A》、《J. Number Theory》和《中国科学·数学》上发表论文十五篇。2019年,受邀请在第八届世界华人数学家大会上作了45分钟报告。主持过国家自然科学基金青年项目和安徽省自然科学基金面上项目,以及参与科技部重点研发计划和科技创新2030重大项目。
When can a binary expander code correct 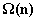 errors in
errors in 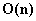 time
time
上官冲
山东大学
Tanner codes are graph-based linear codes whose parity-check matrices can be characterized by a bipartite graph 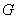 together with an inner code
together with an inner code 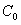 . Expander codes are Tanner codes whose defining bipartite graph
. Expander codes are Tanner codes whose defining bipartite graph 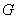 has good expansion property. The landmark work of Sipser and Spielman showed that every bipartite vertex expander
has good expansion property. The landmark work of Sipser and Spielman showed that every bipartite vertex expander 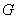 with vertex expansion ratio
with vertex expansion ratio 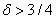 together with a parity-check code defines an expander code that corrects
together with a parity-check code defines an expander code that corrects 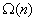 errors in
errors in 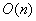 time, where
time, where 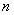 is the code length. Viderman showed that
is the code length. Viderman showed that 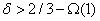 is already sufficient. Our paper is motivated by the following natural and fundamental problem in decoding expander codes:
is already sufficient. Our paper is motivated by the following natural and fundamental problem in decoding expander codes:
Question: What are the sufficient and necessary conditions that  and
and 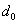 should satisfy so that every bipartite expander
should satisfy so that every bipartite expander 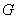 with expansion ratio
with expansion ratio  and every inner code
and every inner code 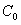 with minimum distance
with minimum distance 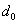 together define an expander code that corrects
together define an expander code that corrects 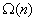 errors in
errors in 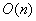 time?
time?
We give a near-optimal solution to the question above, showing that  is sufficient and
is sufficient and 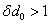 is necessary. Our result significantly improves the previously known result of Dowling and Gao, who showed that
is necessary. Our result significantly improves the previously known result of Dowling and Gao, who showed that 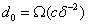 is sufficient, where
is sufficient, where 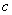 is the left-degree of
is the left-degree of 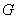 . We suspect that
. We suspect that 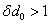 is also sufficient to solve the question above.
is also sufficient to solve the question above.
Based on a joint work with Kuan Cheng (PKU), Minghui Ouyang (PKU), and my PhD student Yuanting Shen (SDU).
个人简介:上官冲,山东大学数学与交叉科学研究中心教授、博士生导师,主要从事组合数学与信息科学交叉领域的研究,在组合数学与图论专业期刊《Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series A》、《Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B》、《SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics》,理论计算机科学顶尖会议与期刊 STOC、FOCS、《SIAM Journal on Computing》,以及信息论与编码理论的旗舰期刊《IEEE Transactions on Information Theory》等相关领域的国际知名刊物上发表论文二十余篇。获得国际组合数学及其应用协会(Institute of Combinatorics and its Applications) Kirkman 奖,入选国家海外高层次青年专家项目。
Exploiting the Symmetry of 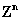 :
:
Randomization and the Automorphism Problem
王安宇
清华大学
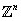 is one of the simplest types of lattices, but the computational problems on its rotations, such as
is one of the simplest types of lattices, but the computational problems on its rotations, such as 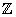 SVP and
SVP and 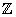 LIP, have been of great interest in cryptography. Recent advances have been made in building cryptographic primitives based on these problems, as well as in developing new algorithms for solving them. However, the theoretical complexity of
LIP, have been of great interest in cryptography. Recent advances have been made in building cryptographic primitives based on these problems, as well as in developing new algorithms for solving them. However, the theoretical complexity of 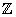 SVP and
SVP and 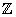 LIP are still not well understood.
LIP are still not well understood.
In this presentation, we explore the issues related to rotations of 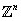 by leveraging their symmetry property. We introduce a randomization framework that can be roughly viewed as ‘applying random automorphisms’ to the output of an oracle, without accessing the automorphism group. Using this framework, we obtain new reduction results for rotations of
by leveraging their symmetry property. We introduce a randomization framework that can be roughly viewed as ‘applying random automorphisms’ to the output of an oracle, without accessing the automorphism group. Using this framework, we obtain new reduction results for rotations of 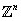 . First, we present a reduction from
. First, we present a reduction from 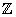 LIP to
LIP to 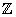 SCVP. Here
SCVP. Here 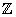 SCVP is the problem of finding the shortest characteristic vectors, which is a special case of CVP where the target vector is a deep hole of the lattice. Moreover, we prove a reduction from
SCVP is the problem of finding the shortest characteristic vectors, which is a special case of CVP where the target vector is a deep hole of the lattice. Moreover, we prove a reduction from 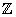 SVP to
SVP to 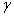 -
-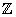 SVP for any constant
SVP for any constant 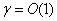 in the same dimension, which implies that
in the same dimension, which implies that 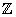 SVP is as hard as its approximate version for any constant approximation factor. Second, we investigate the problem of finding a nontrivial automorphism for a given lattice, which is called LAP. Specifically, we use the randomization framework to show that
SVP is as hard as its approximate version for any constant approximation factor. Second, we investigate the problem of finding a nontrivial automorphism for a given lattice, which is called LAP. Specifically, we use the randomization framework to show that 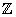 LAP is as hard as
LAP is as hard as 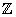 LIP.
LIP.
个人简介:王安宇,清华大学高等研究院副研究员,主要从事密码和编码理论的研究,在密码三大顶会CRYPTO、EUROCRYPT、ASIACRYPT以及IEEE Transactions on Information Theory、CHES等高水平刊物上以第一或通讯作者身份发表多篇论文,获2023年亚密会最佳论文奖,是中国密码学会首届推荐入选中国科协“青年人才托举工程”的青年学者之一,曾获中国科学院信息工程研究所“引进优秀青年人才”专项经费支持,作为子课题负责人或项目骨干参与科技部国家重点研发计划、工信部工业互联网创新发展工程等重要课题,担任了中国密码学会第三届青年工作委员会委员等学术职务。
Large Atomic Model
王涵
北京应用物理与计算数学研究所
Machine learning assisted modeling of interatomic potential energy functions is radically changing the field of molecular simulation. With the accumulation of high-quality electronic structure data, it is expected that a model can be pre-trained on all available data and fine-tuned on downstream tasks, enabling rapid deployment and application with minimal additional effort. We propose the Large Atomic Model (LAM) architecture, training methods, fine-tuning strategies, and model knowledge distillation techniques, and preliminarily establish the corresponding workflow. At the model architecture level, we developed the DPA-2 model architecture based on message passing and attention mechanisms, which achieved better results in potential energy function modeling tasks than existing model architectures. We developed multi-task training methods to solve the problem of inability to jointly train first-principles data from different fields, greatly improving the model's generalization capabilities. Our tests in practical application systems show that even with only the lowest 0.25% of training data, the fine-tuning-distillation model application effect can be fully comparable to the model trained from scratch on the full dataset. The construction of the Large Atomic Model requires an open and collaborative community environment. Therefore, we propose the Open Large Atomic Model Project, OpenLAM, and we welcome the audience to participate in the development and contribution of OpenLAM in any way.
个人简介:Han Wang, Professor at the Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Ph.D. supervisor. He graduated from the School of Mathematical Sciences at Peking University in 2011, obtaining a Doctor of Science degree. From 2011 to 2014, he conducted postdoctoral research at the Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science at the Free University of Berlin. In 2014, he joined the Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics. His main research interests are multiscale modeling and computational methods in molecular dynamics simulations.
Prompt as Triggers for Backdoor Attack: Examining the Vulnerability in Language Models
温金明
暨南大学
The prompt-based learning paradigm, which bridges the gap between pre-training and fine-tuning, achieves state-of-the-art performance on several NLP tasks, particularly in few-shot settings. Despite being widely applied, prompt-based learning is vulnerable to backdoor attacks. Textual backdoor attacks are designed to introduce targeted vulnerabilities into models by poisoning a subset of training samples through trigger injection and label modification. However, they suffer from flaws such as abnormal natural language expressions resulting from the trigger and incorrect labeling of poisoned samples. In this study, we propose ProAttack, a novel and efficient method for performing clean-label backdoor attacks based on the prompt, which uses the prompt itself as a trigger. Our method does not require external triggers and ensures correct labeling of poisoned samples, improving the stealthy nature of the backdoor attack. With extensive experiments on rich-resource and few-shot text classification tasks, we empirically validate ProAttack's competitive performance in textual backdoor attacks. Notably, in the rich-resource setting, ProAttack achieves state-of-the-art attack success rates in the clean-label backdoor attack benchmark without external triggers.
个人简介:温金明,2015年6月博士毕业于加拿大麦吉尔大学数学与统计学院,从2015年3月到2018年8月,先后在法国科学院里昂并行计算实验室、加拿大阿尔伯塔大学、多伦多大学从事博士后研究工作。2018年9月起在暨南大学工作,现任暨南大学三级教授、博士生导师、国家高层次青年人才、广东省青年珠江学者,中国数学会理事、人工智能学会离散智能计算专委会常务委员兼副秘书长、广东省工业与应用数学学会理事、广东省计算数学学会理事,近5年主持国家自然科学基金3项、省级项目4项。温教授的研究方向是整数信号和稀疏信号恢复的算法设计与理论分析,近年来以第一作者/通讯作者在Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis、Inverse Problem、IEEE Transactions on Information Theory、IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing等期刊和会议发表60余篇学术论文。
Cryptanalysis of the Peregrine Lattice-Based Signature Scheme
喻杨
清华大学
Peregrine 签名是韩国后量子密码标准竞赛算法之一。作为美国 NIST 后量子签名标准算法 Falcon 的高速变体, Peregrine 将 Falcon 签名过程中的 NTRU 格高斯采样算法替换成基于中心二项分布的新型采样算法。这一改动大幅简化算法实现并提升签名效率,但是无法保证签名算法的可证明安全性。
本工作中,我们给出 Peregrine 签名的实际密钥恢复攻击。我们注意到 Peregrine 签名分布是已知分布在经过密钥矩阵线性变换后所得。基于 Nguyen-Regev 平行多面体学习攻击的思想,我们证明可以通过分析 Peregrine 签名的统计量获取密钥向量的近似。进一步,结合 Prest 解码技术可完全恢复签名密钥。我们实验证实了攻击的有效性:给定 25000 (11000000) 个Peregrine签名样本,我们能够以高概率在数小时内恢复出 Peregrine-512 参考实现(官方描述)的密钥。该工作发表在公钥密码学国际顶级会议 PKC 2024。
个人简介:喻杨,清华大学高等研究院副研究员,分别于2013年、2018年于清华大学计算机系获学士、博士学位。主要研究方向为格密码,包括格密码算法分析与设计、格基约化算法研究等。近年来在Journal of Cryptology, Crypto, Eurocrypt, Asiacrypt, PKC, CHES等密码领域权威期刊、会议发表论文十余篇。入选国家级青年人才计划和中国科协“青年人才托举工程”项目,主持国家自然科学基金1项,重点研发计划课题1项,核心参与天元数学前沿重点专项。获Asiacrypt 2023最佳论文(2篇),Asiacrypt 2018最佳论文提名。

